Known for their power, agility, and regal appearance, big cats are enormous, carnivorous felines that belong to the genus Panthera and other groupings. Lions, tigers, leopards, jaguars, and snow Big Cats are among them; cheetahs and cougars are frequently compared because of their size and traits. As apex predators, big cats are essential to preserving the equilibrium of the environment. Having adapted to a variety of environments, including savannas, woods, and mountains, they display exceptional hunting abilities as well as distinctive habits, such as the communal prides of lions or the solitary nature of tigers. Conservation efforts are essential to preserving these amazing animals since habitat degradation, poaching, and human conflict threaten their survival.
Table of Contents
Physical Traits and Adaptation
Leopards may be disguised in a variety of settings because to their golden fur, which is easily recognized and has black dots or rosettes. They range in size from 80 to 200 and are both extremely heavy and extremely mobile, traits that are ingrained in their powerful legs for climbing trees and pulling prey from other scavengers’ fronts. Big cats with this coat color are known as melanistic black panthers, and under some circumstances, they may still be identified by their disc-shaped markings.
Habitat and Range
The majority of people are unaware that big cats are versatile animals that can survive in a variety of settings. Leopards may be found in portions of India, China, and Russia, as well as in dry sub-Saharan Africa and tropical rainforests and mountains. Leopards may live near humans and are aggressive, which leads to conflict, unlike many other large felids. They are said to be among the most adaptive big cats due to their environmental adaptability.
Diet and Hunting Skills
Leopards are opportunistic predators who exploit the darkness. They can eat anything from mice to birds, although they favor medium-sized mammals like warthogs, antelopes, and deer. One characteristic that sets Big Cats apart is their propensity to pull their victims into trees in order to shield them from other predators. Since Big Cats are mostly nocturnal creatures, they would eagerly pursue their prey at night because of their exceptional ability to move around in the dark without being easily seen. Leopard facts that emphasize their status as apex predators are best illustrated by these hunting abilities.
Solitary Behavior and Reproduction
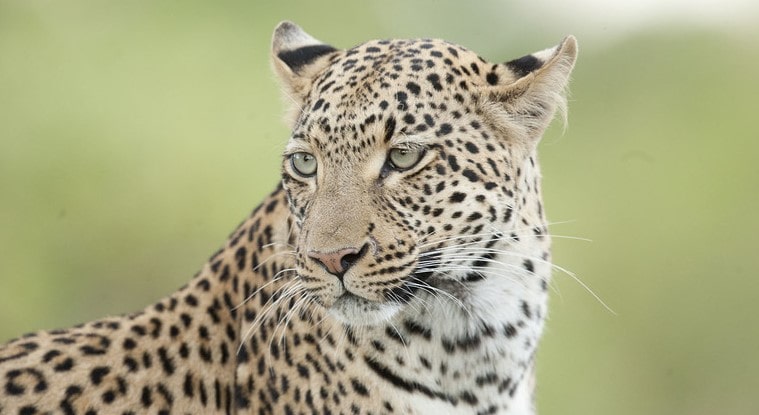

Leopards are mostly territorial animals that mark out their territory by using scent and tree scratch marks. Males tend to larger areas that they may share with several females. Leopards communicate using gestures, low growling tones, vocalizations, scent spraying, and sawing noises. Females give birth to one to three cubs after three months of pregnancy, and in order to keep them safe, they frequently abandon them in the higher grass. Before becoming independent, cubs spend up to two years with their mother, learning how to hunt, locate food, and mark their territory.
Conservation and Threats
The IUCN Red List has classified leopards as “Vulnerable,” with risks ranging from poaching and wildlife trade to habitat degradation and human-leopard conflict. Leopards face dangers and conflict due to their growing numbers; they are being sought for their use in traditional medicine. Although there are regulations protecting Big Cats the last thing that can be stated is that, especially in the wilderness, it is difficult, if not impossible, to put the laws into operation. The primary challenge faced by captive leopards is that they lack the complex surroundings necessary for their survival.
Importance of Leopards in Ecosystems
Apex predators like leopards keep the ecology in balance. They help increase flora and other wildlife while keeping herbivores under control and lowering the likelihood of overgrazing. They are referred to as “umbrella species,” which means that any other species that live in these environments will likewise be protected if theirs is. Understanding these leopard facts is much more crucial because it is our responsibility to protect them in order to support successful conservation.
Born Free’s Role in Leopard Conservation
The Born Free Foundation works to protect leopards and their habitat, particularly by advocating for stricter regulations on trophy hunting and the rehabilitation of leopards kept in inhumane conditions in captivity. In South Africa, there is a big cat Sanctuary dedicated to caring for rescued leopards so they may continue living their natural lives. These include Adopt, Shop, and Donate, which contributes to the funding of conservation animal rescue; a direct donation helps raise awareness and educate the public about coexisting with leopards.
How You Can Make a Difference

Therefore, worldwide action is required to save Big Cats . You may join them and contribute to the protection of these amazing animals and their habitats because of organizations like Born Free. Raising awareness is equally as important in guaranteeing that leopard will continue to attract attention in the years to come, even while the public can make more concrete contributions like direct donations, adopting a leopard, or making financial contributions. By highlighting these important facts, you may encourage others to act as well. Visit Born Free to find out more about how you can contribute to the conservation of leopards.
Final Thoughts
Big cats are stunning creatures that stand for both grace and might at the same time. Ecosystems depend on adaptability and the capacity for hunting. We are getting closer to realizing that leopards still exist on our planet because to the work of groups like Born Free. Their efforts consistently bring attention to the need to maintain biodiversity among various species in the natural environment.